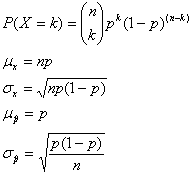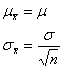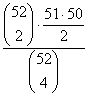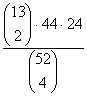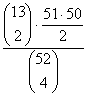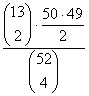|
STAtistics / Mr. Hansen |
Name:
_________________________ |
Test #5
Probability, Type I/Type II error, sampling
distributions, and simulations
Time limit: 34 minutes (51 for extended time).
|
Useful Formulae: |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
P(A È B) = P(A)
+ P(B) – P(A Ç B) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E(X) = mX = S xi pi |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If X has a binomial distribution with parameters n and p, then: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inferential Statistics |
|
|
|
Standardized statistic: Confidence interval: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
Suppose that there is a
population from which we will plan to take a random sample. What term have we
been using for the distribution of data in the population? |
|
|
|
(A) underlying data
distribution |
(D) sampling distribution |
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
A t distribution with df = 20 has what
shape? |
|
|
|
(A) normal (z) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
The abbreviation df stands for _____ and equals _____ in the case of the
sampling distribution of |
|
|
|
(A) degrees of freedom, n – 1 |
(D) distribution of
factors, n |
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
How are the sampling
distribution of |
|
|
|
(A) t and normal, respectively |
(D) binomial and t, respectively |
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
The Student’s t distribution came from what field? |
|
|
|
(A) tobacco |
(D) brewing |
|
|
|
|
|
6. |
We poll an SRS of 500
voters in a large city and discover that 322 of them think that Candidate Jones
is supercilious. A writer for the city newspaper estimates that the true
proportion of voters in the city who think Candidate Jones is supercilious is
between 60% and 65%. With what confidence can she make this statement? |
|
|
|
(A) 55% |
(D) 68% |
|
|
|
|
|
7. |
By default (i.e., unless
otherwise stated), political polls in The
Washington Post that are reported with a margin of error have a
confidence level of . . . |
|
|
|
(A) 90% |
(D) 99.9% |
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
I hope that my true mean
diastolic blood pressure is no more than 80 mm Hg. Over a period of time, I
take 5 measurements at random intervals and find a mean of 78 mm Hg with a
standard deviation of 6 mm Hg. With what confidence can I assert that my true
mean diastolic blood pressure is less than or equal to 80 mm Hg? |
|
|
|
(A) 63% |
(D) 98% |
|
|
|
|
|
9. |
I hope that my true mean diastolic
blood pressure is no more than 80 mm Hg. Over a period of time, I take 40
measurements at random intervals and find a mean of 78 mm Hg with a standard
deviation of 6 mm Hg. With what confidence can I assert that my true mean
diastolic blood pressure is less than or equal to 80 mm Hg? |
|
|
|
(A) 63% |
(D) 98% |
|
|
|
|
|
10. |
The four themes of our course
are exploratory data analysis, design of studies, probability, and _____ , and the latter can be summarized as _____ . |
|
|
|
(A) hypothesis testing,
computing probabilities of Type I and Type II errors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
11. |
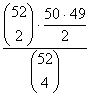
If 4 cards are drawn
without replacement from a well-shuffled deck, compute the probability that
there is exactly one pair (not two pair, not 3 of a kind, not 4 of a kind). |
|
|
|
(A) |
(D) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12. |
In a screening test for high
blood pressure, we will recommend a doctor for anyone whose systolic pressure
is above 130 mm Hg or whose diastolic pressure is above 80 mm Hg in a single
test reading. State the null and alternative hypotheses. |
|
|
|
(A) H0: systolic £ 130 and diastolic £ 80; Ha:
systolic > 130 and diastolic > 80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
13. |
In #12, what would
constitute Type I and Type II error, respectively? |
|
|
|
(A) needless referral to a doctor,
missed diagnosis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
14. |
We perform an Excel-based simulation
of a complex industrial process that involves 52 steps. If any one of the
steps fails, we call the simulated batch a “failure”; otherwise, it is a
“success.” Which of the following is true as we summarize our findings of
5,000,000 simulated trials? |
|
|
|
(A) |
(D) |
|
|
|
|
|
15. |
Lung cancer among
nonsmokers is rare. Let us assume that P(lung cancer | nonsmoker) = 0.0019 for the sake of this
problem. If the probability of smoking is .22 and the probability of lung
cancer given smoking is .18, compute the probability of lung cancer in the
overall population. |
|
|
|
(A) 0.036 |
(D) 0.040 |